Build a dashboard#
What is the purpose of this page?
This tutorial is meant to get your hands dirty with building a Lumen dashboard. Don’t worry about understanding everything just yet - your only obligation is to complete the steps as directed.
You will build a simple Lumen dashboard and deploy it in your browser. The result will look something like this:
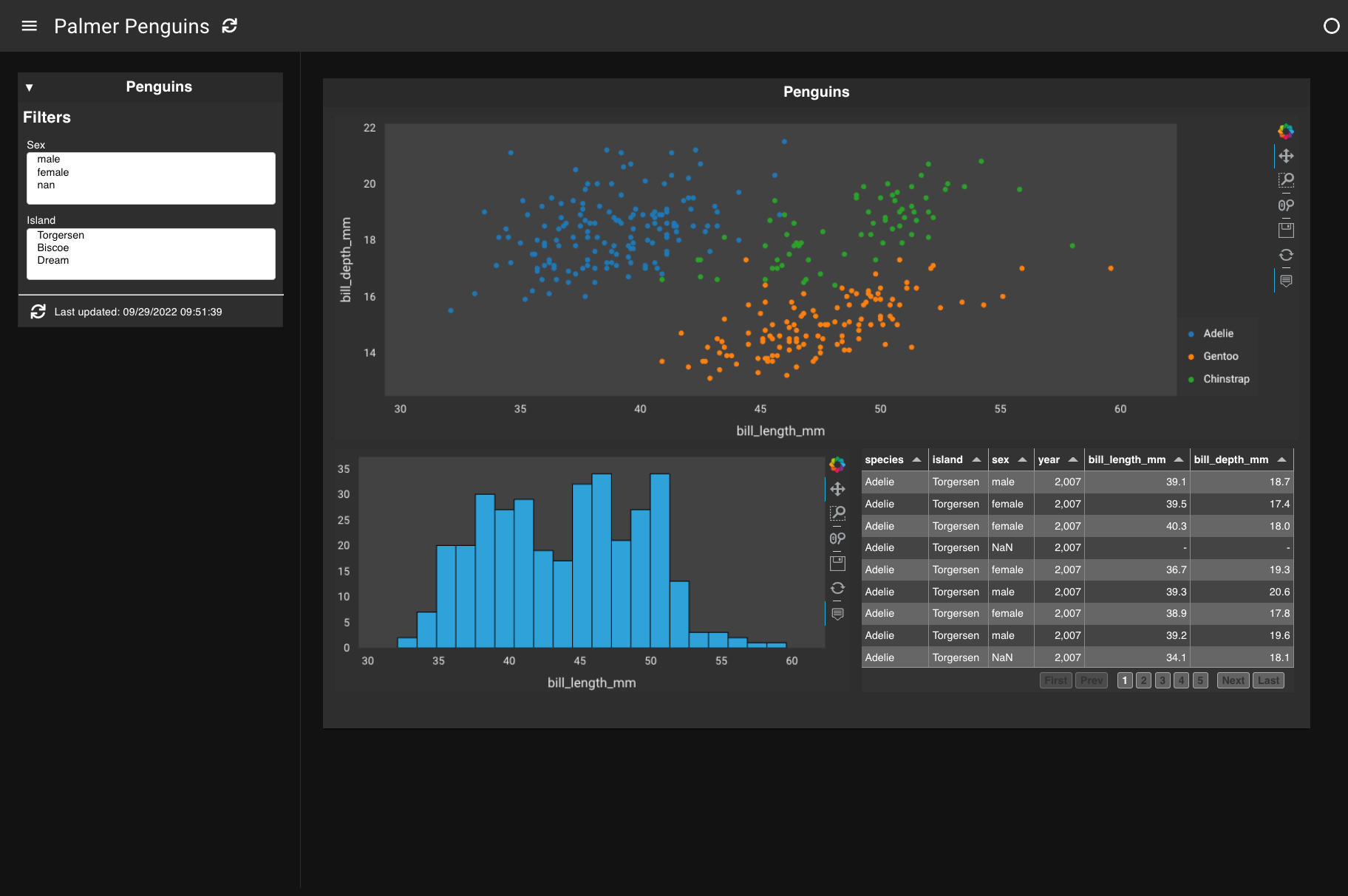
1. Create a YAML file#
Open your favorite text editor and create an empty file called penguins.yaml.
2. Add a data source#
The first thing that is needed is a source of data. Insert and save the text below to add a remote FileSource. This will tell Lumen to fetch the Palmer Penguins dataset:
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
Once you have saved your file, open a terminal and navigate to the location of this file.
In the terminal, launch the file with:
lumen serve penguins.yaml --show --autoreload
By using --autoreload, the dashboard automatically updates the application whenever we make changes to the YAML file.
What you should see in your browser should now match what is on the Preview tab:
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
So far, this returns an empty dashboard because we haven’t yet specified a view - so let’s add one!
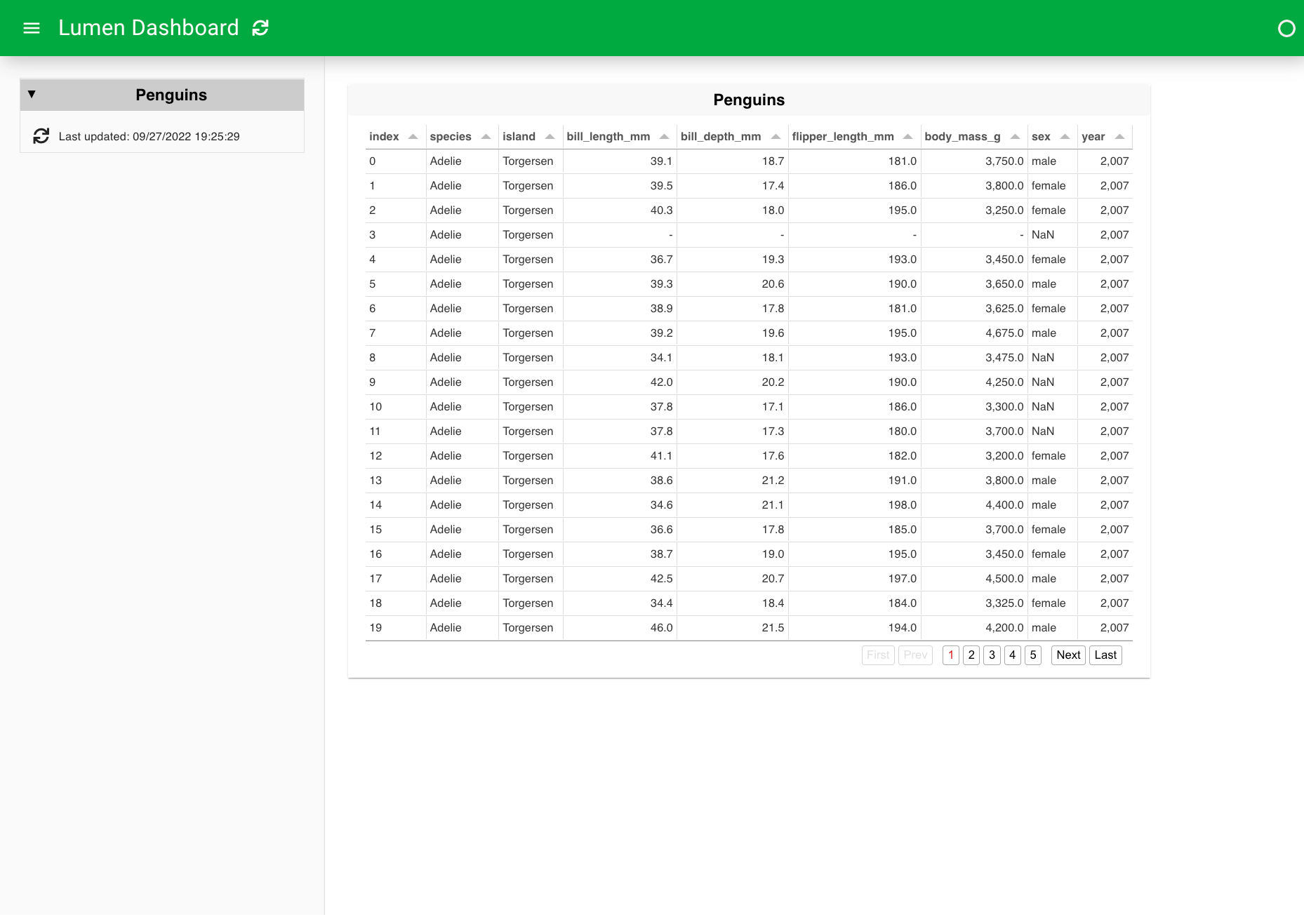
3. Specify a table view#
The simplest View to add is a table with the raw data. This gives us a good idea of what we are working with and the available fields.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
layouts:
- title: Penguins
source: penguin_source
views:
- type: table
table: penguin_table
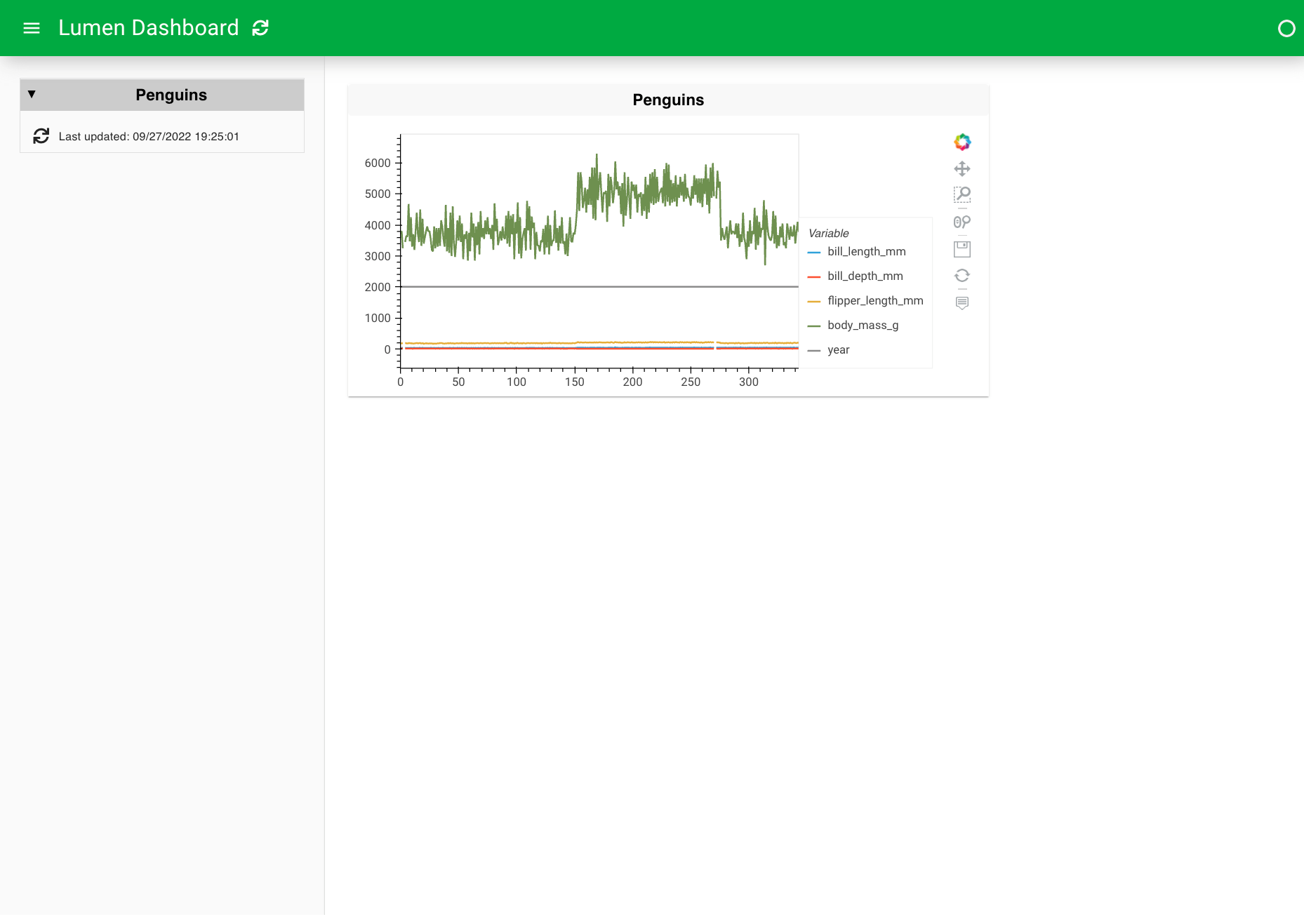
4. Create a plot view#
The table gives us a primer of the data source, but to start understanding patterns in the data, we have to visualize it. There is a wide range of views to chose from but for now we will create an hvPlotView (see hvPlot for background on the library). This is as easy as replacing the table type with a hvplot type.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
layouts:
- title: Penguins
source: penguin_source
views:
- type: hvplot
table: penguin_table
5. Make a scatter plot#
This plot is a bit overwhelming, so instead of plotting everything in one plot, we can plot bill_length_mm on the x-axis and bill_depth_mm on the y-axis. Furthermore, we can color based on the species and change the kind of the plot to scatter.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
layouts:
- title: Penguins
source: penguin_source
views:
- type: hvplot
table: penguin_table
kind: scatter
x: bill_length_mm
y: bill_depth_mm
color: species
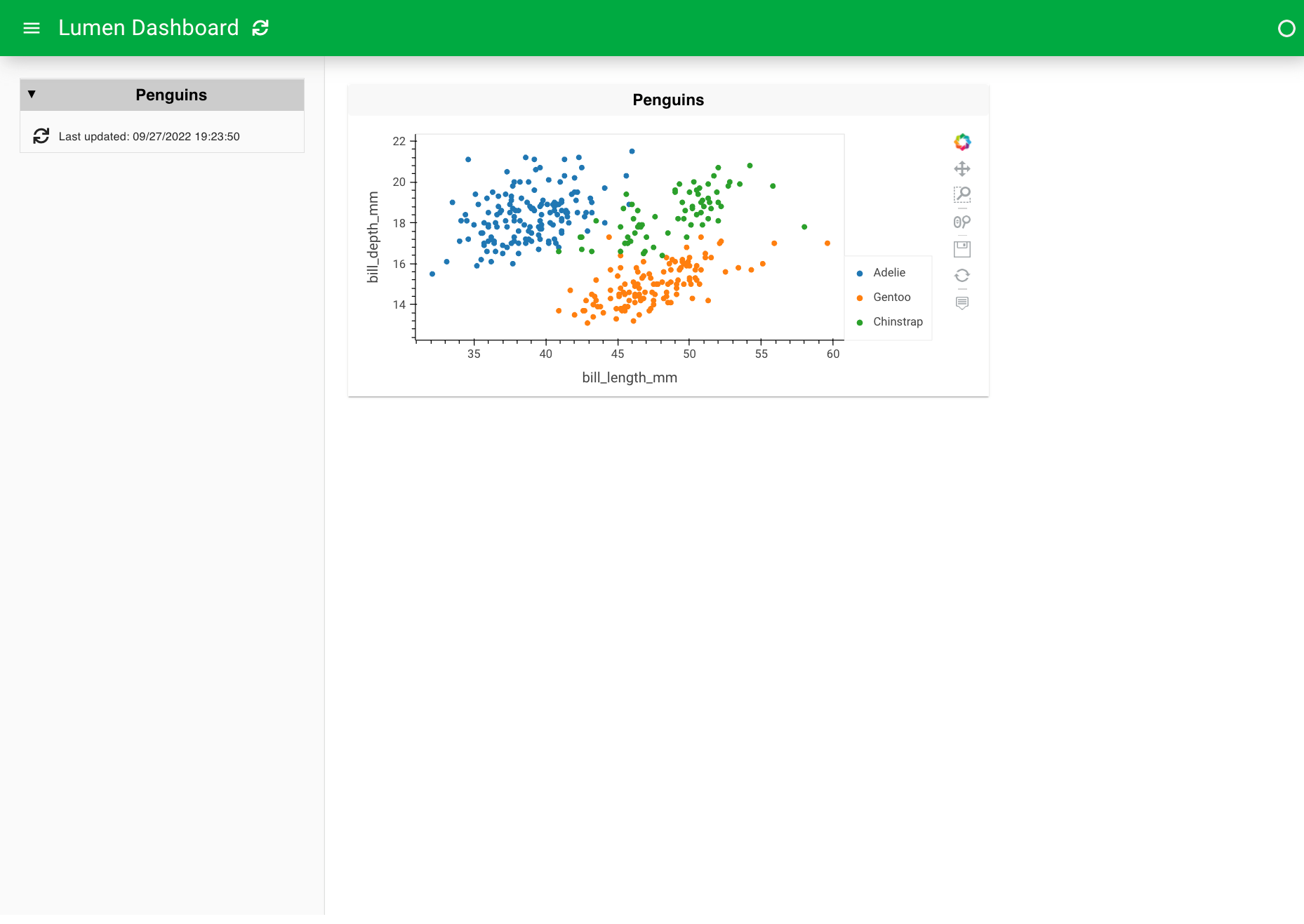
6. Manipulate the data#
Let’s now set up two filter widgets based on two fields of the data - ‘sex’ and ‘island’. Since we don’t need all of the data columns, let’s also add a transform to select only a subset of the data.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
pipelines:
penguin_pipeline:
source: penguin_source
table: penguin_table
filters:
- type: widget
field: sex
- type: widget
field: island
transforms:
- type: columns
columns: ['species', 'island', 'sex', 'year', 'bill_length_mm', 'bill_depth_mm']
layouts:
- title: Penguins
pipeline: penguin_pipeline
views:
- type: hvplot
x: bill_length_mm
y: bill_depth_mm
kind: scatter
color: species
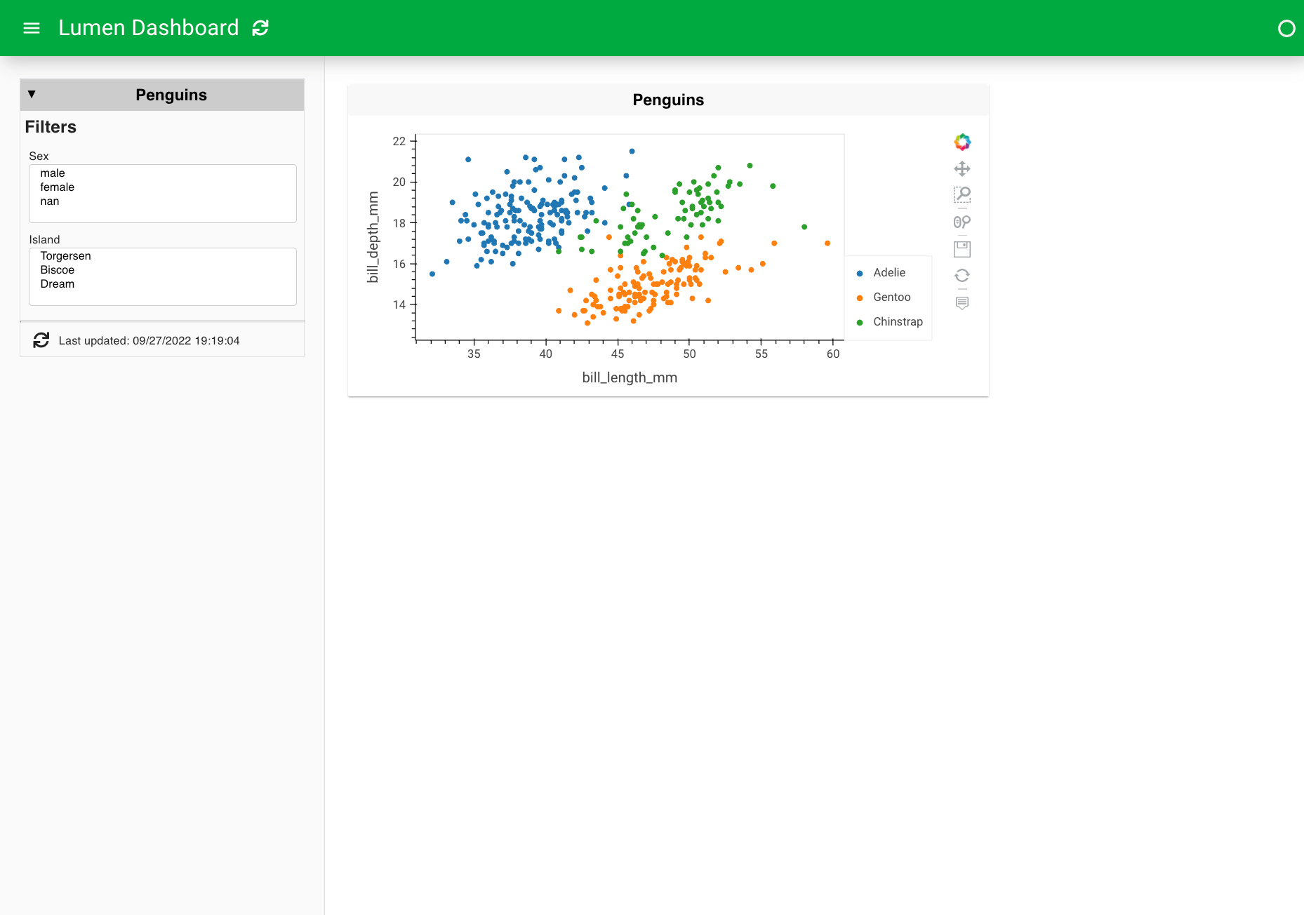
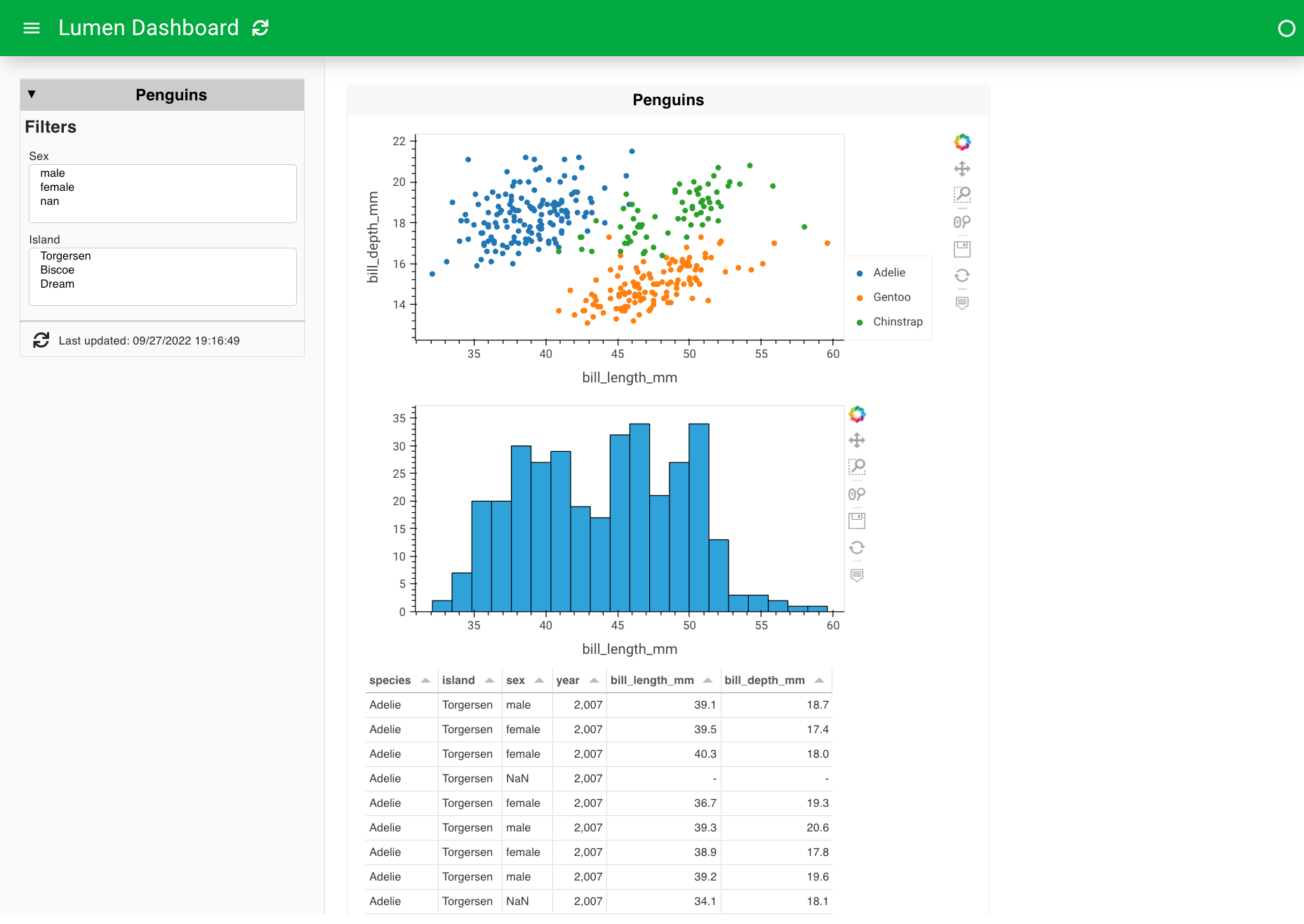
7. Expand the view types#
We can even expand the views with a histogram and a table.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
pipelines:
penguin_pipeline:
source: penguin_source
table: penguin_table
filters:
- type: widget
field: sex
- type: widget
field: island
transforms:
- type: columns
columns: ['species', 'island', 'sex', 'year', 'bill_length_mm', 'bill_depth_mm']
layouts:
- title: Penguins
pipeline: penguin_pipeline
views:
- type: hvplot
x: bill_length_mm
y: bill_depth_mm
kind: scatter
color: species
- type: hvplot
kind: hist
y: bill_length_mm
- type: table
show_index: false
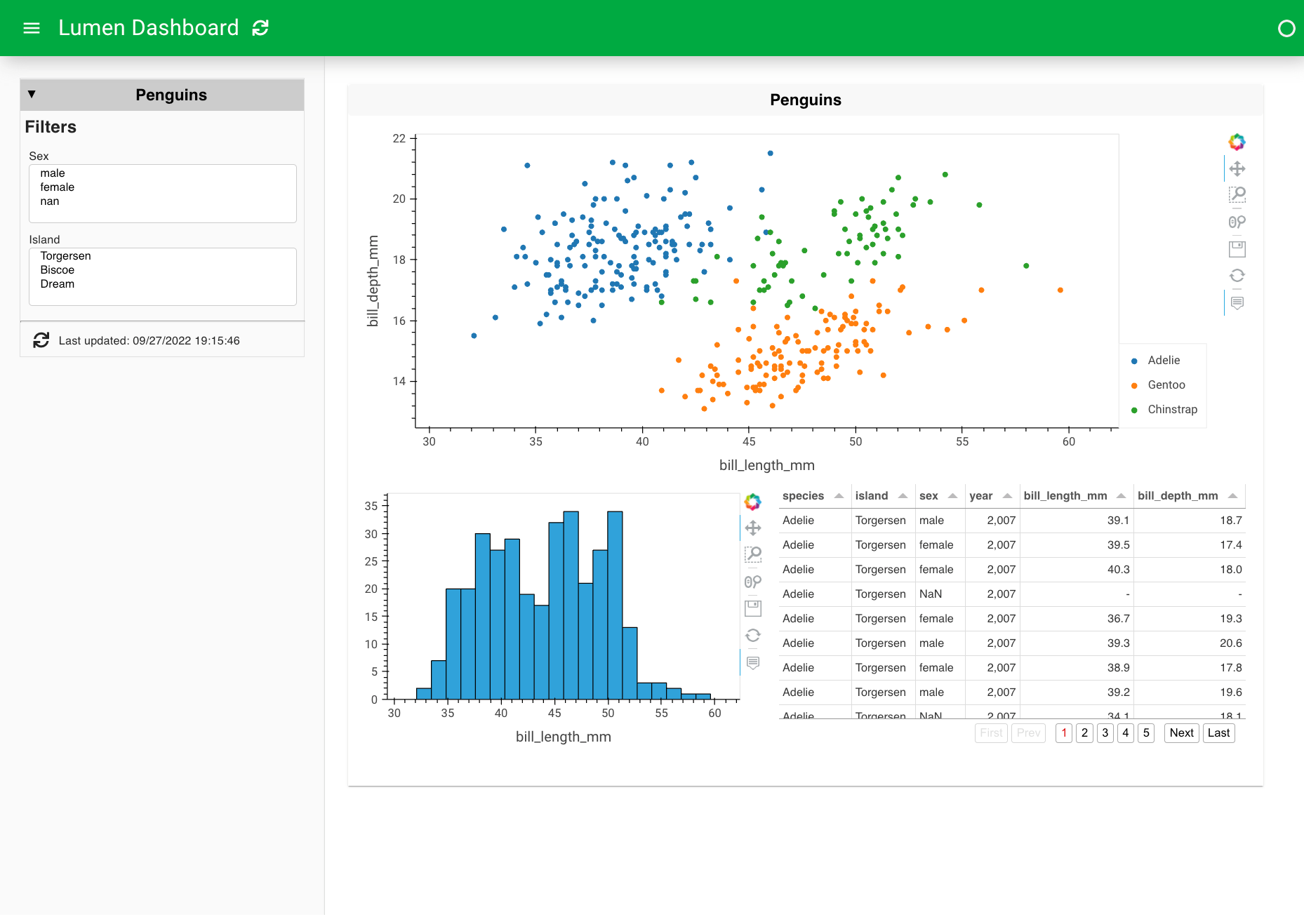
8. Customize the appearance and behavior#
The default layout we get is less than ideal for this case since it cuts off one of our plots, leaves a lot of empty space, and does not resize responsively. We can get responsive plots by adding sizing_mode to the layout and responsive to the views. By changing the layout and height, we can further customize how the dashboard looks.
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
pipelines:
penguin_pipeline:
source: penguin_source
table: penguin_table
filters:
- type: widget
field: sex
- type: widget
field: island
transforms:
- type: columns
columns: ['species', 'island', 'sex', 'year', 'bill_length_mm', 'bill_depth_mm']
layouts:
- title: Penguins
pipeline: penguin_pipeline
layout: [[0], [1, 2]]
sizing_mode: stretch_width
height: 800
views:
- type: hvplot
x: bill_length_mm
y: bill_depth_mm
kind: scatter
color: species
responsive: true
height: 400
- type: hvplot
kind: hist
y: bill_length_mm
responsive: true
height: 300
- type: table
show_index: false
height: 300
9. Add a title and theme#
Final step - let’s use a config section to give our dashboard a more descriptive title and change the overall theme to dark. Note that we can also set our table to dark by adding a new theme parameter at the bottom.
config:
title: Palmer Penguins
theme: dark
sources:
penguin_source:
type: file
tables:
penguin_table: https://datasets.holoviz.org/penguins/v1/penguins.csv
pipelines:
penguin_pipeline:
source: penguin_source
table: penguin_table
filters:
- type: widget
field: sex
- type: widget
field: island
transforms:
- type: columns
columns: ['species', 'island', 'sex', 'year', 'bill_length_mm', 'bill_depth_mm']
layouts:
- title: Penguins
pipeline: penguin_pipeline
layout: [[0], [1, 2]]
sizing_mode: stretch_width
height: 800
views:
- type: hvplot
x: bill_length_mm
y: bill_depth_mm
kind: scatter
color: species
responsive: true
height: 400
- type: hvplot
kind: hist
y: bill_length_mm
responsive: true
height: 300
- type: table
show_index: false
height: 300
theme: midnight

Congratulations! You have created your first Lumen dashboard and know a bit more about penguins!
Note
This is just a simple example of how to build a dashboard with Lumen. The next step is to review the core concepts of what we just achieved so you can generalize these steps to create your own dashboard.
